时间:2021-07-01 10:21:17 帮助过:21人阅读
方法1:
使用数据库客户端(SSMS)的界面工具。右键选择要导出数据的数据库,选择“任务”——“导出数据”,下图1,按照向导一步一步操作即可。而导入则相反,导入时,SQLServer会默认创建一张新表,字段名也默认跟导入的Excel标题一样,并且会默认字段数据类型等。当然在可以在向导进行修改。需要注意的是如果标题不是英文而是中文,默认创建字段名也是中文,这将给后面数据更新操作带来麻烦,所以最好还是以有意义的英文字段名。把数据导入后,再通过执行语句,把数据插入/更新到业务表。
figure-1:任务——导出数据
方法2:
从SQLServer2005开始,可以直接在SSMS上查询出来的结果复制,然后粘贴到Excel上,对于少量数据来说,是非常快速方便的,需要注意的是长数字可能会变成科学记数法的形式,提前在Excel上指定列的格式为文本即可。
导入的话,ctrl + c 复制Excel上的数据,然后在选择相关表,编辑数据,把数据直接粘贴上去即可。但是不建议直接粘贴到业务表(如果表是空白没有数据,并且字段顺序对应,可以这样操作),而是建议先粘贴到一个新建的中间表中,然后再通过语句,把数据插入/更新到业务表。
这种方法的导出导入,适合于少量的数据,如5000行以内的记录,大于5000行以上就不建议了,速度较慢,如果数据过大,还一定成功。
(二)数据库与文本文件、数据库与数据库
数据库之间的数据迁移或导出导入其实是比较方便的,比如备份数据库后,在新的机器上做恢复。但是需要注意的是SQL2008之前的版本的备份无法在SQL2012或以上版本上直接恢复的,而是通过中间的SQL2008做一个过渡,把旧版本的数据库恢复到SQL2008,然后做备份,最后在SQL2012上恢复。
如果是新版本(下面以SQL2012为例)的备份文件恢复到旧版本(以SQL2008为例)上就比较麻烦了,一般是不支持新版本备份文件在旧版本中恢复的。只能通过编写脚本,把新版本的数据导入到旧版本中。
方法1:
首先推荐使用的是数据不落地的“链接服务器”。使用SQL2012的SSMS,同时连接到SQL2012和SQL2008的实例,通过编写脚本把SQL2012的数据导入到SQL2008中。两个实例的可以通过链接服务器来连接。以下是设置步骤。
figure-2:新建链接服务器
figure-3:链接服务器和数据源
figure-4:认证
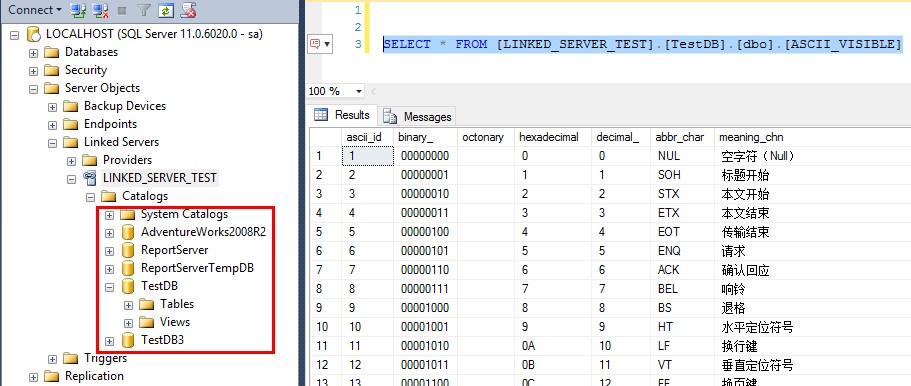
figure-5:创建成功后,可以直接浏览链接服务器的目录,也可以使用语句查询了。
也可以使用脚本来创建链接服务器。
--创建链接服务器 EXEC sp_addlinkedserver @server=‘LINKED_SERVER_TEST2‘,--被访问的服务器别名 @srvproduct=‘‘, @provider=‘SQLOLEDB‘, @datasrc=‘192.168.88.6,11433‘--数据源 GO --创建登录名和密码 EXEC sys.sp_addlinkedsrvlogin @rmtsrvname = ‘LINKED_SERVER_TEST2‘, -- 被访问的服务器别名 @useself = ‘false‘, @locallogin = NULL, @rmtuser = ‘sa‘, -- 数据源登录名 @rmtpassword = ‘psd123456‘ -- 数据源登录密码 GO --设置数据可以访问 EXEC sys.sp_serveroption @server = ‘LINKED_SERVER_TEST2‘, @optname = ‘data access‘, @optvalue = N‘true‘ GO
code-1:创建链接服务器的脚本
创建成功后,可以直接查询数据。
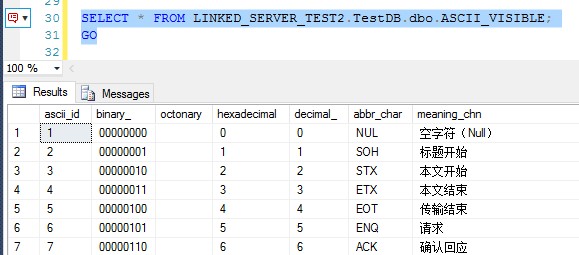
figure-6:查询链接服务器的数据
通过视图sys.servers可以查询所有服务器及相关的属性。
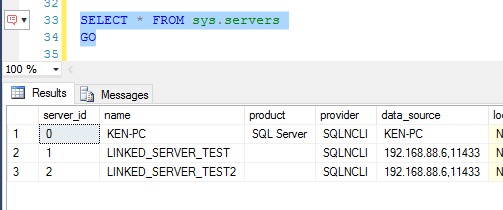
figure-7:查询所有链接服务器
在SSMS上或运行以下脚本可以删除指定的链接服务器。
--删除链接服务器及所有登录 EXEC sys.sp_dropserver @server = ‘LINKED_SERVER_TEST2‘, @droplogins = ‘droplogins‘ GO
code-2:删除链接服务器及所有登录
详细请参考:https://technet.microsoft.com/zh-cn/library/ff772782%28v=sql.105%29.aspx
方法2:
如果两个实例不能连接,只能在SQL2012上导出数据,再到SQL2008上导入。SQLServer提供生成包含数据的脚本工具,下图2。在第三步的“高级”选项里有一项“Types of data to scripts”有三个选择:Data only,Schema and data,Schema only,分别是只生成数据、生成表(对象)和数据,表(对象)。还有生成脚本的版本“Script for Server Version”,下图3。其他选项,按实际需要选择。
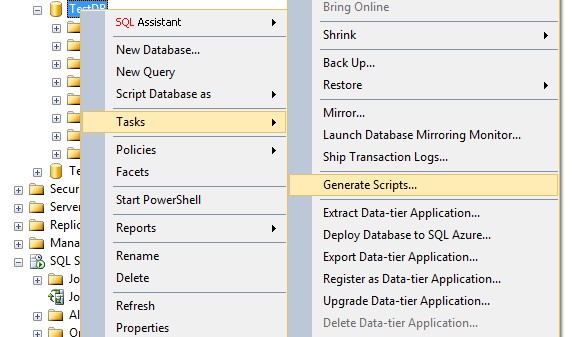
figure-8:任务——生成脚本
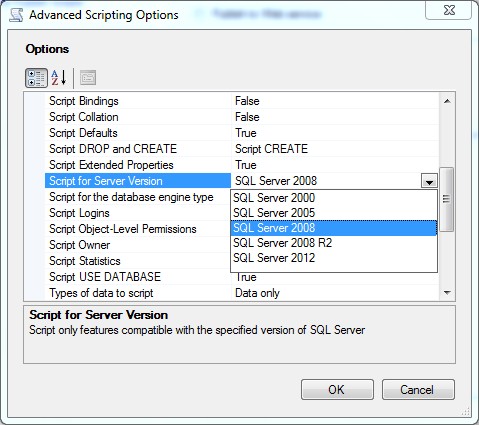
figure-9:生成脚本的高级选项
也可以使用存储过程生成包含数据的脚本。这里介绍一个别人已经做写好存储过程:sp_generate_inserts。运行之后,会按表每条记录生成一条insert的语句
CREATE PROC [dbo].[sp_generate_inserts] ( @table_name VARCHAR(776) , -- The table/view for which the INSERT statements will be generated using the existing data @target_table VARCHAR(776) = NULL , -- Use this parameter to specify a different table name into which the data will be inserted @include_column_list BIT = 1 , -- Use this parameter to include/ommit column list in the generated INSERT statement @from VARCHAR(800) = NULL , -- Use this parameter to filter the rows based on a filter condition (using WHERE) @include_timestamp BIT = 0 , -- Specify 1 for this parameter, if you want to include the TIMESTAMP/ROWVERSION column‘s data in the INSERT statement @debug_mode BIT = 0 , -- If @debug_mode is set to 1, the SQL statements constructed by this procedure will be printed for later examination @owner VARCHAR(64) = NULL , -- Use this parameter if you are not the owner of the table @ommit_images BIT = 0 , -- Use this parameter to generate INSERT statements by omitting the ‘image‘ columns @ommit_identity BIT = 1 , -- Use this parameter to ommit the identity columns @top INT = NULL , -- Use this parameter to generate INSERT statements only for the TOP n rows @cols_to_include VARCHAR(8000) = NULL , -- List of columns to be included in the INSERT statement @cols_to_exclude VARCHAR(8000) = NULL , -- List of columns to be excluded from the INSERT statement @disable_constraints BIT = 0 , -- When 1, disables foreign key constraints and enables them after the INSERT statements @ommit_computed_cols BIT = 1 -- When 1, computed columns will not be included in the INSERT statement ) AS BEGIN /*********************************************************************************************************** Procedure: sp_generate_inserts (Build 22) (Copyright ?2002 Narayana Vyas Kondreddi. All rights reserved.) Purpose: To generate INSERT statements from existing data. These INSERTS can be executed to regenerate the data at some other location. This procedure is also useful to create a database setup, where in you can script your data along with your table definitions. Written by: Narayana Vyas Kondreddi http://vyaskn.tripod.com Acknowledgements: Divya Kalra -- For beta testing Mark Charsley -- For reporting a problem with scripting uniqueidentifier columns with NULL values Artur Zeygman -- For helping me simplify a bit of code for handling non-dbo owned tables Joris Laperre -- For reporting a regression bug in handling text/ntext columns Tested on: SQL Server 7.0 and SQL Server 2000 Date created: January 17th 2001 21:52 GMT Date modified: May 1st 2002 19:50 GMT Email: vyaskn@hotmail.com NOTE: This procedure may not work with tables with too many columns. Results can be unpredictable with huge text columns or SQL Server 2000‘s sql_variant data types Whenever possible, Use @include_column_list parameter to ommit column list in the INSERT statement, for better results IMPORTANT: This procedure is not tested with internation data (Extended characters or Unicode). If needed you might want to convert the datatypes of character variables in this procedure to their respective unicode counterparts like nchar and nvarchar Example 1: To generate INSERT statements for table ‘titles‘: EXEC sp_generate_inserts ‘titles‘ Example 2: To ommit the column list in the INSERT statement: (Column list is included by default) IMPORTANT: If you have too many columns, you are advised to ommit column list, as shown below, to avoid erroneous results EXEC sp_generate_inserts ‘titles‘, @include_column_list = 0 Example 3: To generate INSERT statements for ‘titlesCopy‘ table from ‘titles‘ table: EXEC sp_generate_inserts ‘titles‘, ‘titlesCopy‘ Example 4: To generate INSERT statements for ‘titles‘ table for only those titles which contain the word ‘Computer‘ in them: NOTE: Do not complicate the FROM or WHERE clause here. It‘s assumed that you are good with T-SQL if you are using this parameter EXEC sp_generate_inserts ‘titles‘, @from = "from titles where title like ‘%Computer%‘" Example 5: To specify that you want to include TIMESTAMP column‘s data as well in the INSERT statement: (By default TIMESTAMP column‘s data is not scripted) EXEC sp_generate_inserts ‘titles‘, @include_timestamp = 1 Example 6: To print the debug information: EXEC sp_generate_inserts ‘titles‘, @debug_mode = 1 Example 7: If you are not the owner of the table, use @owner parameter to specify the owner name To use this option, you must have SELECT permissions on that table EXEC sp_generate_inserts Nickstable, @owner = ‘Nick‘ Example 8: To generate INSERT statements for the rest of the columns excluding images When using this otion, DO NOT set @include_column_list parameter to 0. EXEC sp_generate_inserts imgtable, @ommit_images = 1 Example 9: To generate INSERT statements excluding (ommiting) IDENTITY columns: (By default IDENTITY columns are included in the INSERT statement) EXEC sp_generate_inserts mytable, @ommit_identity = 1 Example 10: To generate INSERT statements for the TOP 10 rows in the table: EXEC sp_generate_inserts mytable, @top = 10 Example 11: To generate INSERT statements with only those columns you want: EXEC sp_generate_inserts titles, @cols_to_include = "‘title‘,‘title_id‘,‘au_id‘" Example 12: To generate INSERT statements by omitting certain columns: EXEC sp_generate_inserts titles, @cols_to_exclude = "‘title‘,‘title_id‘,‘au_id‘" Example 13: To avoid checking the foreign key constraints while loading data with INSERT statements: EXEC sp_generate_inserts titles, @disable_constraints = 1 Example 14: To exclude computed columns from the INSERT statement: EXEC sp_generate_inserts MyTable, @ommit_computed_cols = 1 ***********************************************************************************************************/ SET NOCOUNT ON --Making sure user only uses either @cols_to_include or @cols_to_exclude IF ( ( @cols_to_include IS NOT NULL ) AND ( @cols_to_exclude IS NOT NULL ) ) BEGIN RAISERROR(‘Use either @cols_to_include or @cols_to_exclude. Do not use both the parameters at once‘,16,1) RETURN -1 --Failure. Reason: Both @cols_to_include and @cols_to_exclude parameters are specified END --Making sure the @cols_to_include and @cols_to_exclude parameters are receiving values in proper format IF ( ( @cols_to_include IS NOT NULL ) AND ( PATINDEX(‘‘‘%‘‘‘, @cols_to_include) = 0 ) ) BEGIN RAISERROR(‘Invalid use of @cols_to_include property‘,16,1) PRINT ‘Specify column names surrounded by single quotes and separated by commas‘ PRINT ‘Eg: EXEC sp_generate_inserts titles, @cols_to_include = "‘‘title_id‘‘,‘‘title‘‘"‘ RETURN -1 --Failure. Reason: Invalid use of @cols_to_include property END IF ( ( @cols_to_exclude IS NOT NULL ) AND ( PATINDEX(‘‘‘%‘‘‘, @cols_to_exclude) = 0 ) ) BEGIN RAISERROR(‘Invalid use of @cols_to_exclude property‘,16,1) PRINT ‘Specify column names surrounded by single quotes and separated by commas‘ PRINT ‘Eg: EXEC sp_generate_inserts titles, @cols_to_exclude = "‘‘title_id‘‘,‘‘title‘‘"‘ RETURN -1 --Failure. Reason: Invalid use of @cols_to_exclude property END --Checking to see if the database name is specified along wih the table name --Your database context should be local to the table for which you want to generate INSERT statements --specifying the database name is not allowed IF ( PARSENAME(@table_name, 3) ) IS NOT NULL BEGIN RAISERROR(‘Do not specify the database name. Be in the required database and just specify the table name.‘,16,1) RETURN -1 --Failure. Reason: Database name is specified along with the table name, which is not allowed END --Checking for the existence of ‘user table‘ or ‘view‘ --This procedure is not written to work on system tables --To script the data in system tables, just create a view on the system tables and script the view instead IF @owner IS NULL BEGIN IF ( ( OBJECT_ID(@table_name, ‘U‘) IS NULL ) AND ( OBJECT_ID(@table_name, ‘V‘) IS NULL ) ) BEGIN RAISERROR(‘User table or view not found.‘,16,1) PRINT ‘You may see this error, if you are not the owner of this table or view. In that case use @owner parameter to specify the owner name.‘ PRINT ‘Make sure you have SELECT permission on that table or view.‘ RETURN -1 --Failure. Reason: There is no user table or view with this name END END ELSE BEGIN IF NOT EXISTS ( SELECT 1 FROM INFORMATION_SCHEMA.TABLES WHERE TABLE_NAME = @table_name AND ( TABLE_TYPE = ‘BASE TABLE‘ OR TABLE_TYPE = ‘VIEW‘ ) AND TABLE_SCHEMA = @owner ) BEGIN RAISERROR(‘User table or view not found.‘,16,1) PRINT ‘You may see this error, if you are not the owner of this table. In that case use @owner parameter to specify the owner name.‘ PRINT ‘Make sure you have SELECT permission on that table or view.‘ RETURN -1 --Failure. Reason: There is no user table or view with this name END END --Variable declarations DECLARE @Column_ID INT , @Column_List NVARCHAR(MAX) , @Column_Name VARCHAR(128) , @Start_Insert NVARCHAR(MAX) , @Data_Type VARCHAR(128) , @Actual_Values NVARCHAR(MAX) , --This is the string that will be finally executed to generate INSERT statements @IDN VARCHAR(128) --Will contain the IDENTITY column‘s name in the table --Variable Initialization SET @IDN = ‘‘ SET @Column_ID = 0 SET @Column_Name = ‘‘ SET @Column_List = ‘‘ SET @Actual_Values = ‘‘ IF @owner IS NULL BEGIN SET @Start_Insert = ‘INSERT INTO ‘ + ‘[‘ + RTRIM(COALESCE(@target_table, @table_name)) + ‘]‘ END ELSE BEGIN SET @Start_Insert = ‘INSERT ‘ + ‘[‘ + LTRIM(RTRIM(@owner)) + ‘].‘ + ‘[‘ + RTRIM(COALESCE(@target_table, @table_name)) + ‘]‘ END --To get the first column‘s ID SELECT @Column_ID = MIN(ORDINAL_POSITION) FROM INFORMATION_SCHEMA.COLUMNS (NOLOCK) WHERE TABLE_NAME = @table_name AND ( @owner IS NULL OR TABLE_SCHEMA = @owner ) --Loop through all the columns of the table, to get the column names and their data types WHILE @Column_ID IS NOT NULL BEGIN SELECT @Column_Name = QUOTENAME(COLUMN_NAME) , @Data_Type = DATA_TYPE FROM INFORMATION_SCHEMA.COLUMNS (NOLOCK) WHERE ORDINAL_POSITION = @Column_ID AND TABLE_NAME = @table_name AND ( @owner IS NULL OR TABLE_SCHEMA = @owner ) IF @cols_to_include IS NOT NULL --Selecting only user specified columns BEGIN IF CHARINDEX(‘‘‘‘ + SUBSTRING(@Column_Name, 2, LEN(@Column_Name) - 2) + ‘‘‘‘, @cols_to_include) = 0 BEGIN GOTO SKIP_LOOP END END IF @cols_to_exclude IS NOT NULL --Selecting only user specified columns BEGIN IF CHARINDEX(‘‘‘‘ + SUBSTRING(@Column_Name, 2, LEN(@Column_Name) - 2) + ‘‘‘‘, @cols_to_exclude) <> 0 BEGIN GOTO SKIP_LOOP END END --Making sure to output SET IDENTITY_INSERT ON/OFF in case the table has an IDENTITY column IF ( SELECT COLUMNPROPERTY(OBJECT_ID(QUOTENAME(COALESCE(@owner, USER_NAME())) + ‘.‘ + @table_name), SUBSTRING(@Column_Name, 2, LEN(@Column_Name) - 2), ‘IsIdentity‘) ) = 1 BEGIN IF @ommit_identity = 0 --Determing whether to include or exclude the IDENTITY column SET @IDN = @Column_Name ELSE GOTO SKIP_LOOP END --Making sure whether to output computed columns or not IF @ommit_computed_cols = 1 BEGIN IF ( SELECT COLUMNPROPERTY(OBJECT_ID(QUOTENAME(COALESCE(@owner, USER_NAME())) + ‘.‘ + @table_name), SUBSTRING(@Column_Name, 2, LEN(@Column_Name) - 2), ‘IsComputed‘) ) = 1 BEGIN GOTO SKIP_LOOP END END --Tables with columns of IMAGE data type are not supported for obvious reasons IF ( @Data_Type IN ( ‘image‘ ) ) BEGIN IF ( @ommit_images = 0 ) BEGIN RAISERROR(‘Tables with image columns are not supported.‘,16,1) PRINT ‘Use @ommit_images = 1 parameter to generate INSERTs for the rest of the columns.‘ PRINT ‘DO NOT ommit Column List in the INSERT statements. If you ommit column list using @include_column_list=0, the generated INSERTs will fail.‘ RETURN -1 --Failure. Reason: There is a column with image data type END ELSE BEGIN GOTO SKIP_LOOP END END --Determining the data type of the column and depending on the data type, the VALUES part of --the INSERT statement is generated. Care is taken to handle columns with NULL values. Also --making sure, not to lose any data from flot, real, money, smallmomey, datetime columns SET @Actual_Values = @Actual_Values + CASE WHEN @Data_Type IN ( ‘char‘, ‘varchar‘, ‘nchar‘,‘nvarchar‘ ) THEN ‘COALESCE(‘‘N‘‘‘‘‘‘ + REPLACE(RTRIM(‘ + @Column_Name + ‘),‘‘‘‘‘‘‘‘,‘‘‘‘‘‘‘‘‘‘‘‘)+‘‘‘‘‘‘‘‘,‘‘NULL‘‘)‘ WHEN @Data_Type IN ( ‘datetime‘, ‘smalldatetime‘,