时间:2021-07-01 10:21:17 帮助过:54人阅读
Searches for a server parameter file in a platform-specific default location and, if not found, for a text initialization parameter file (specifying STARTUP with the SPFILE or PFILE parameters overrides the default behavior)
Reads the parameter file to determine the values of initialization parameters
Allocates the SGA based on the initialization parameter settings
Starts the Oracle background processes
Opens the alert log and trace files and writes all explicit parameter settings to the alert log in valid parameter syntax
2) 数据库被mount
实例被启动,打开数据库的控制文件关联一个数据库。数据库对用户还是close状态。对就的命令是alter database mount;
To mount the database, the instance obtains the names of the database control files specified in the CONTROL_FILES initialization parameter and opens the files. Oracle Database reads the control files to find the names of the data files and the online redo log files that it will attempt to access when opening the database.
In a mounted database, the database is closed and accessible only to database administrators. Administrators can keep the database closed while completing specific maintenance operations. However, the database is not available for normal operations.
3) 数据库被open
实例被启动,关联的数据库被open。数据库中的数据可以被用户访问。对应的命令是alter database open。
Opens the online data files in tablespaces other than undo tablespaces
If a tablespace was offline when the database was previously shut down (see "Online and Offline Tablespaces"), then the tablespace and its corresponding data files will be offline when the database reopens.
Acquires an undo tablespace
If multiple undo tablespaces exists, then the UNDO_TABLESPACE initialization parameter designates the undo tablespace to use. If this parameter is not set, then the first available undo tablespace is chosen.
Opens the online redo log files
2、Oracle实例和数据库的关闭
通常关闭Oracle数据库使用sqlplus执行shutdown命令
再看官方给的图:
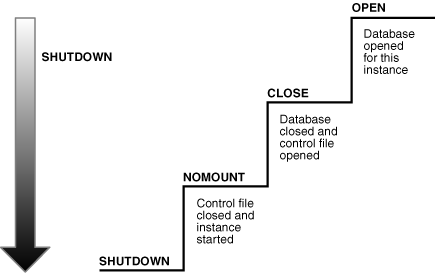
从上图中也可以看出从数据库open状态到shutdown状态也经历三个阶段:
1) 数据库被关闭
数据库还是mount状态,但在线数据文件和日志文件被关闭了。
The database close operation is implicit in a database shutdown. The nature of the operation depends on whether the database shutdown is normal or abnormal.
When a database is closed as part of a SHUTDOWN with any option other than ABORT, Oracle Database writes data in the SGA to the data files and online redo log files. Next, the database closes online data files and online redo log files. Any offline data files of offline tablespaces have been closed already. When the database reopens, any tablespace that was offline remains offline.
At this stage, the database is closed and inaccessible for normal operations. The control files remain open after a database is closed.
SHUTDOWN ABORT or abnormal termination occurs, then the instance of an open database closes and shuts down the database instantaneously. Oracle Database does not write data in the buffers of the SGA to the data files and redo log files. The subsequent reopening of the database requires instance recovery, which Oracle Database performs automatically.2) 数据库被umount
实例是启动的,但不再通过控制文件关联数据库。
After the database is closed, Oracle Database unmounts the database to disassociate it from the instance. After a database is unmounted, Oracle Database closes the control files of the database. At this point, the instance remains in memory.
3) 实例被shutdown
实例被shutdown。
The final step in database shutdown is shutting down the instance. When the database instance is shut down, the SGA is removed from memory and the background processes are terminated.
数据库关闭的4种模式:ABORT、IMMEDIATE、TRANSACTIONAL、NORMAL。下面的表格介绍了各模式下数据库的行为。
| Database Behavior | ABORT | IMMEDIATE | TRANSACTIONAL | NORMAL |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Permits new user connections | No | No | No | No |
Waits until current sessions end | No | No | No | Yes |
Waits until current transactions end | No | No | Yes | Yes |
Performs a checkpoint and closes open files | No | Yes | Yes | Yes |
SHUTDOWN ABORT
This mode is intended for emergency situations, such as when no other form of shutdown is successful. This mode of shutdown is the fastest. However, a subsequent open of this database may take substantially longer because instance recovery must be performed to make the data files consistent.
Note:
Because SHUTDOWN ABORT does not checkpoint the open data files, instance recovery is necessary before the database can reopen. The other shutdown modes do not require instance recovery before the database can reopen.
SHUTDOWN IMMEDIATE
This mode is typically the fastest next to SHUTDOWN ABORT. Oracle Database terminates any executing SQL statements and disconnects users. Active transactions are terminated and uncommitted changes are rolled back.
SHUTDOWN TRANSACTIONAL
This mode prevents users from starting new transactions, but waits for all current transactions to complete before shutting down. This mode can take a significant amount of time depending on the nature of the current transactions.
SHUTDOWN NORMAL
This is the default mode of shutdown. The database waits for all connected users to disconnect before shutting down.
下面通过实例演示Oracle数据库的启动和关闭过程,例子中Oracle版本为11.2.0.1
1、启动数据库
当前没有任何进程和共享内存,设置好ORACLE_SID和ORACLE_HOME环境变量
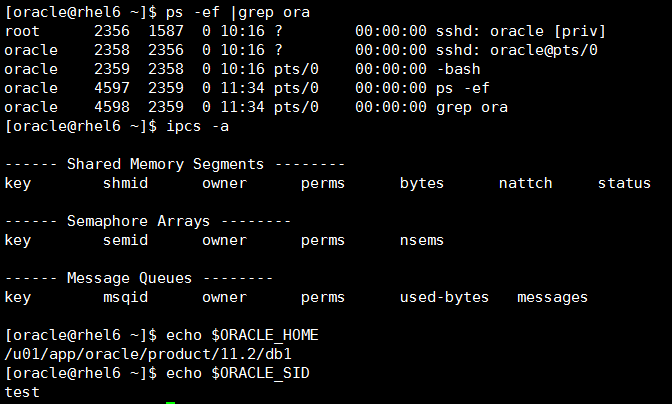
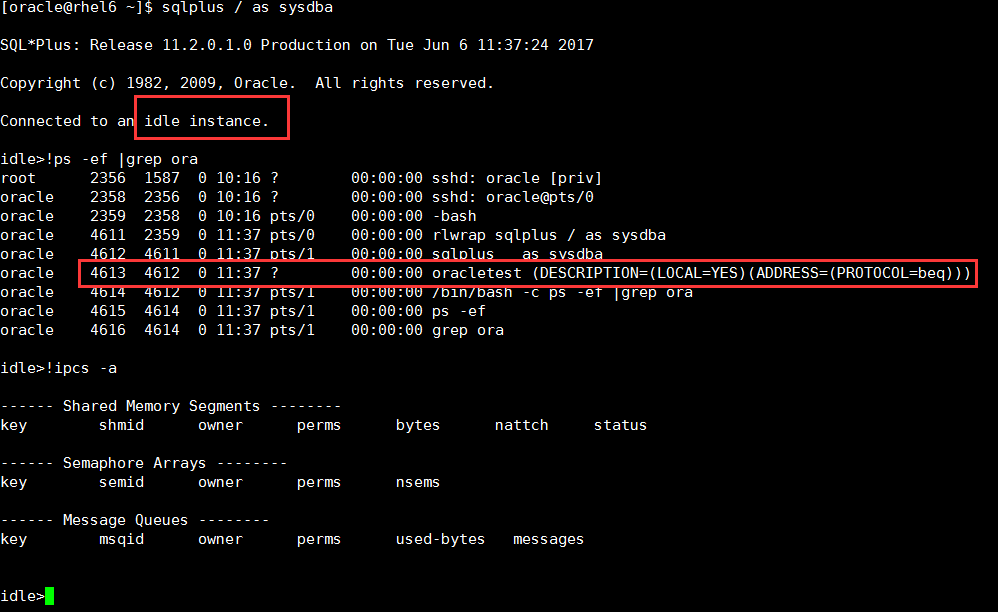
执行sqlplus / as sysdba连接到一个空实例,当前仍然没有共享内存,只增加了一个进程oracletest的进程
使用startup nomount启动数据库实例,该命令默认查找spfile参数文件启动实例,也可以使用startup nomount pfile=‘/dir/init.ora‘指定参数文件启动,在内存中分配共享内存并创建后台进程。
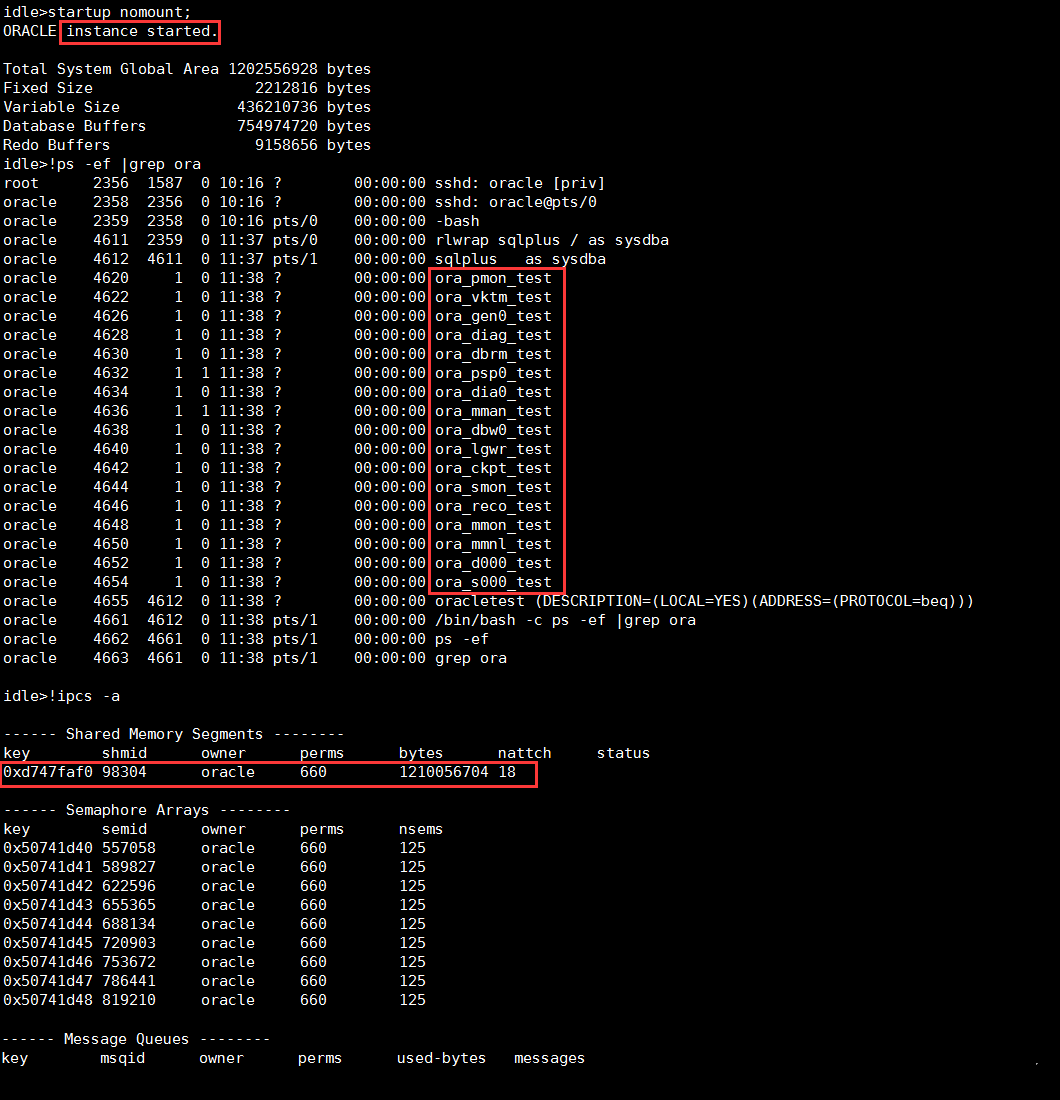 查看当前的实例状态,当前状态只能查少量的视图如v$instance,但大部分视图无法查询如v$database、v$datafile,会报错:ORA-01507: database not mounted
查看当前的实例状态,当前状态只能查少量的视图如v$instance,但大部分视图无法查询如v$database、v$datafile,会报错:ORA-01507: database not mounted
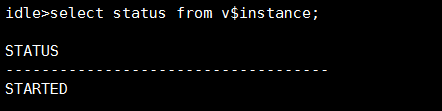
使用alter database mount命令mount数据库,这种状态只能查询部分视图,dba开头的大部分视图都不能查询会报错:ORA-01219: database not open: queries allowed on fixed tables/views only
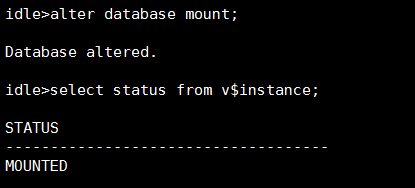
使用alter database open命令open数据库:
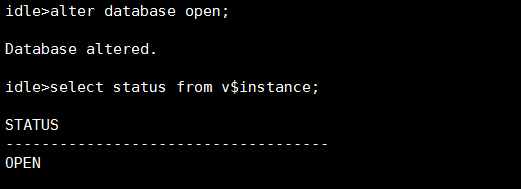
当前数据库被打开,可以对外提供服务。
2、关闭数据库
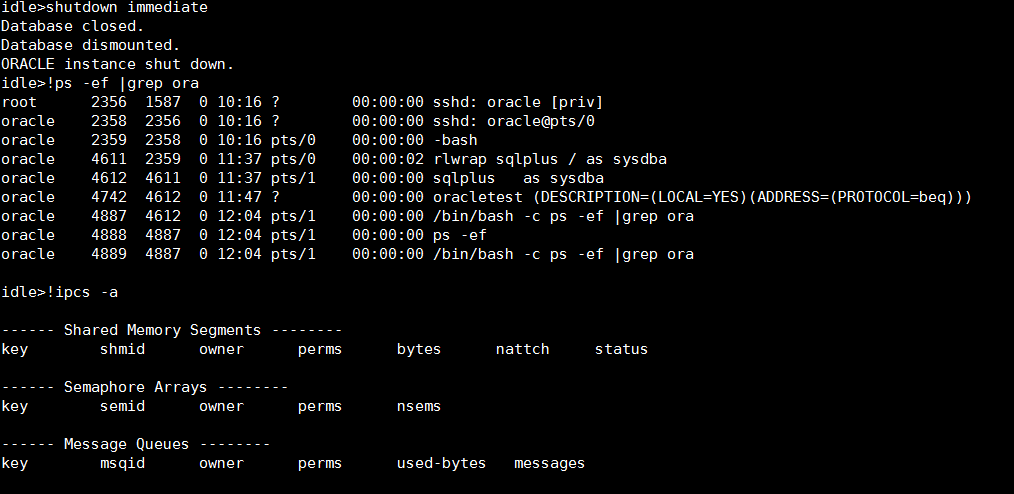 整个启动和关闭的过程都会记录在alert日志文件中。11g的alert日志目录是$ORACLE_BASE/diag/rdbms/dbname/sid/trace。文件名为alert_sid.log。
整个启动和关闭的过程都会记录在alert日志文件中。11g的alert日志目录是$ORACLE_BASE/diag/rdbms/dbname/sid/trace。文件名为alert_sid.log。
参考:http://docs.oracle.com/cd/E11882_01/server.112/e40540/startup.htm#CNCPT89043
《9I10G11G编程艺术 深入数据库体系结构 》
本文出自 “DBA Fighting!” 博客,请务必保留此出处http://hbxztc.blog.51cto.com/1587495/1932703
Oracle数据库启动和关闭
标签:oracle 启动 关闭