时间:2021-07-01 10:21:17 帮助过:10人阅读

# 增加一条记录 person = {‘name‘: ‘zone‘,‘sex‘:‘boy‘} person_id = test.insert_one(person).inserted_id print(person_id) # 批量插入 persons = [{‘name‘: ‘zone‘, ‘sex‘: ‘boy‘}, {‘name‘: ‘zone1‘, ‘sex‘: ‘boy1‘}] result = test.insert_many(persons) print(result.inserted_ids)View Code

# 删除单条记录 result1 = test.delete_one({‘name‘: ‘zone‘}) pprint.pprint(result1) # 批量删除 result1 = test.delete_many({‘name‘: ‘zone‘}) pprint.pprint(result1)View Code

# 更新单条记录 res = test.update_one({‘name‘: ‘zone‘}, {‘$set‘: {‘sex‘: ‘girl girl‘}}) print(res.matched_count) # 更新多条记录 test.update_many({‘name‘: ‘zone‘}, {‘$set‘: {‘sex‘: ‘girl girl‘}})View Code

# 查找多条记录 pprint.pprint(test.find()) # 添加查找条件 pprint.pprint(test.find({"sex": "boy"}).sort("name"))View Code
如果你是我的老读者,那么你肯定知道我之前的骚操作,就是用爬虫爬去数据之后,用聚合统计结合可视化图表进行数据展示。

aggs = [ {"$match": {"$or" : [{"field1": {"$regex": "regex_str"}}, {"field2": {"$regex": "regex_str"}}]}}, # 正则匹配字段 {"$project": {"field3":1, "field4":1}},# 筛选字段 {"$group": {"_id": {"field3": "$field3", "field4":"$field4"}, "count": {"$sum": 1}}}, # 聚合操作 ] result = test.aggregate(pipeline=aggs)View Code
例子:以分组的方式统计 sex 这个关键词出现的次数,说白了就是统计有多少个男性,多少个女性。

test.aggregate([{‘$group‘: {‘_id‘: ‘$sex‘, ‘weight‘: {‘$sum‘: 1}}}])
View Code
聚合效果图:(秋招季,用Python分析深圳程序员工资有多高?文章配图) 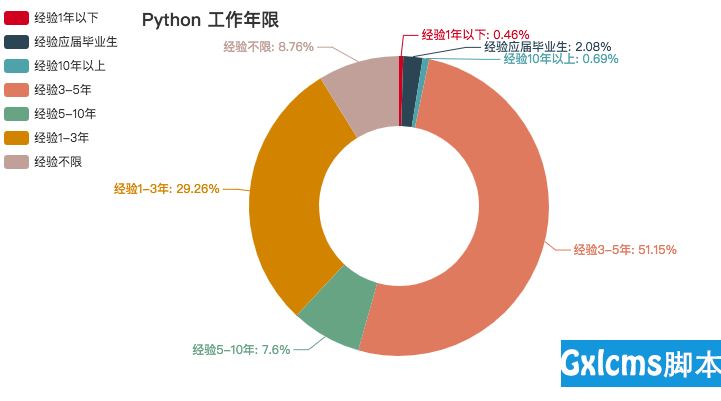

Motor 是一个异步实现的 MongoDB 存储库 Motor 与 Pymongo 的配置基本类似。连接对象就由 MongoClient 变为 AsyncIOMotorClient 了。下面进行详细介绍一下。

# 普通连接 client = motor.motor_asyncio.AsyncIOMotorClient(‘mongodb://localhost:27017‘) # 副本集连接 client = motor.motor_asyncio.AsyncIOMotorClient(‘mongodb://host1,host2/?replicaSet=my-replicaset-name‘) # 密码连接 client = motor.motor_asyncio.AsyncIOMotorClient(‘mongodb://username:password@localhost:27017/dbname‘) # 获取数据库 db = client.zfdb # db = client[‘zfdb‘] # 获取 collection collection = db.test # collection = db[‘test‘]View Code
添加一条记录。

async def do_insert(): document = {‘name‘: ‘zone‘,‘sex‘:‘boy‘} result = await db.test_collection.insert_one(document) print(‘result %s‘ % repr(result.inserted_id)) loop = asyncio.get_event_loop() loop.run_until_complete(do_insert())View Code
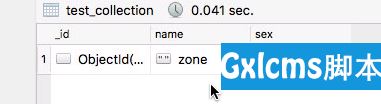
添加结果如图所暗示。

async def do_insert(): result = await db.test_collection.insert_many( [{‘name‘: i, ‘sex‘: str(i + 2)} for i in range(20)]) print(‘inserted %d docs‘ % (len(result.inserted_ids),)) loop = asyncio.get_event_loop() loop.run_until_complete(do_insert())View Code
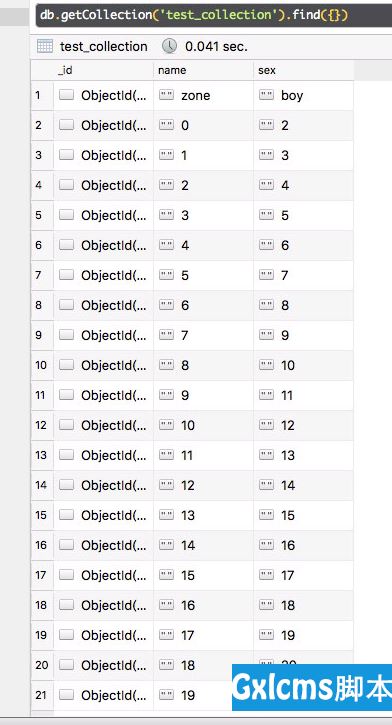

async def do_find_one(): document = await db.test_collection.find_one({‘name‘: ‘zone‘}) pprint.pprint(document) loop = asyncio.get_event_loop() loop.run_until_complete(do_find_one())View Code

查找记录可以添加筛选条件。

async def do_find(): cursor = db.test_collection.find({‘name‘: {‘$lt‘: 5}}).sort(‘i‘) for document in await cursor.to_list(length=100): pprint.pprint(document) loop = asyncio.get_event_loop() loop.run_until_complete(do_find()) # 添加筛选条件,排序、跳过、限制返回结果数 async def do_find(): cursor = db.test_collection.find({‘name‘: {‘$lt‘: 4}}) # Modify the query before iterating cursor.sort(‘name‘, -1).skip(1).limit(2) async for document in cursor: pprint.pprint(document) loop = asyncio.get_event_loop() loop.run_until_complete(do_find())View Code
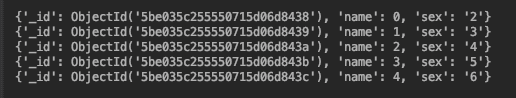

async def do_count(): n = await db.test_collection.count_documents({}) print(‘%s documents in collection‘ % n) n = await db.test_collection.count_documents({‘name‘: {‘$gt‘: 1000}}) print(‘%s documents where i > 1000‘ % n) loop = asyncio.get_event_loop() loop.run_until_complete(do_count())View Code
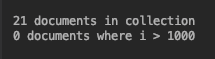
替换则是将除 id 以外的其他内容全部替换掉。

async def do_replace(): coll = db.test_collection old_document = await coll.find_one({‘name‘: ‘zone‘}) print(‘found document: %s‘ % pprint.pformat(old_document)) _id = old_document[‘_id‘] result = await coll.replace_one({‘_id‘: _id}, {‘sex‘: ‘hanson boy‘}) print(‘replaced %s document‘ % result.modified_count) new_document = await coll.find_one({‘_id‘: _id}) print(‘document is now %s‘ % pprint.pformat(new_document)) loop = asyncio.get_event_loop() loop.run_until_complete(do_replace())View Code
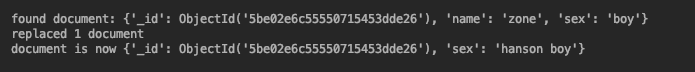
更新指定字段,不会影响到其他内容。

async def do_update(): coll = db.test_collection result = await coll.update_one({‘name‘: 0}, {‘$set‘: {‘sex‘: ‘girl‘}}) print(‘更新条数: %s ‘ % result.modified_count) new_document = await coll.find_one({‘name‘: 0}) print(‘更新结果为: %s‘ % pprint.pformat(new_document)) loop = asyncio.get_event_loop() loop.run_until_complete(do_update())View Code
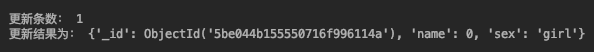
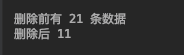
删除指定记录。

async def do_delete_many(): coll = db.test_collection n = await coll.count_documents({}) print(‘删除前有 %s 条数据‘ % n) result = await db.test_collection.delete_many({‘name‘: {‘$gte‘: 10}}) print(‘删除后 %s ‘ % (await coll.count_documents({}))) loop = asyncio.get_event_loop() loop.run_until_complete(do_delete_many())View Code
MongoDB 的骚操作就介绍到这里,后面会继续写 MySQL 和 Redis 的骚操作。尽请期待。

【转】Python操作MongoDB数据库
标签:HERE hid ons cas run async before 工资 pen